Class Outline
1Administration
Computers and Culture
Digitization = Sampling and Quantization
Digitization of Text
Computers and Culture
2Stories that circulate electronically
Upgrading to GirlFriend 4.0 I'm currently running the latest version of GirlFriend and I've been having some problems lately. I've been running the same version of DrinkingBuddies 1.0 forever as my primary application, and all the GirlFriend releases I've tried have always conflicted with it. ...
Urband Legends
Mrs. Fields Cookie legend
What do these tell us about the Internet?
Administration
3Homework - Due Friday!
Web Topic Paper due in two weeks
Hand it print out of rendered HTML and disk with HTML
We care about writing!
Input and Output Model
4Computer as input, processing and output
Digitization is input
What can be digitized?
5Text (Strings of Alphanumeric Characters)
Images (Drawings, Pictures)
Sound (Midi Sequences, Digitized Audio)
Moving Pictures (Video, Animations)
3-D Spaces or Objects (Virtual Reality)
Procedures and Processes
What cannot be digitized?
What is digitization?
6Analog to Digital
Continuous to Multi-level
What is digitization?
7Sampling and Quantization
Digitizing Text
8
How do we digitize texts?
9"Born Digital"
Typing it in
Specialized input tools (Pen Interfaces and Mini-keyboards)
Raw Digitization - OCR
Scanning an image of page
Optical Character Recoginition
This is true of all media!
What is an electronic text?
10A digital file meant to be read
Sequence of characters that are legible when output
A word processing file
Proprietary formats like MS Word
Open formats like PDF
Open text formats
http://www.asciitable.com/ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange
HTML and XML are built on ASCII
ASCII
11Digitization and Codes
All information on the computer is coded
Codes depend on a lookup table
Codes have to be transformed
ASCII Codes are 8 bits
8 bits (one byte) means 256 possibilities
ASCII defines 128 of those (lower ASCII)
Extended ASCII not standardized
Extended ASCII defines upper 128
Digital code can only be interpreted if system knows the code
Raw data is useless unless you know what code system
But, you can transcode!
What do we lose and gain?
12Losses
We lose material presence of paper and print
We lose detail and art of print
Gains
We can duplicate without loss
We can transmit
We can manipulate and transform
Digitizing Images
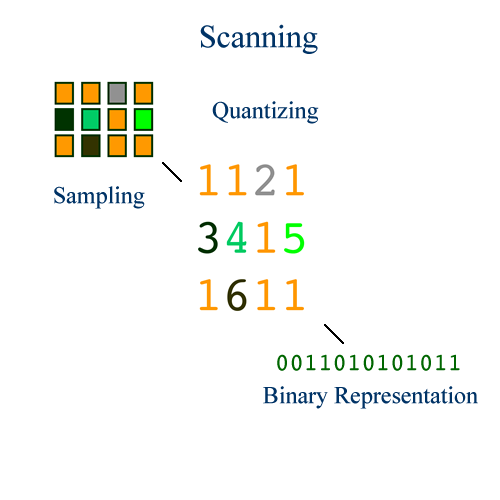
13Sampling and Quantizing
Scanner samples millions of points
Assigns a value to each point based on a colour table
Digital Image
Continuous image converted to bit-map of pixels
Caligraphic to Graphic Screen
14Caligraphic Screen - 80 columns by 60 rows
Monospaced text
No graphics
1984 - Apple Macintosh
Graphic Screen
Bitmap screen where every pixel can be addressed
Screen described as matrix of pixels (Picture Elements)
Even text is now rendered as an image
Digital Cameras
How are they changing the culture of pictures?
Scanning Process
15
Bitmap and Vector
16Two types of images
Bit-map is digitized (Scanner or Digital Camera)
Vector is typically born-digital (Drawing with Mouse)
Bit-map Image
A matrix of pixels (picture elements) each specifying a particular colour or shade of gray.
Vector
A formal description of the shapes to be generated by the computer.
Issues for Images
17Image format
What image format to use?
Resolution
How much resolution do you need?
Colour Depth
What colour depth is needed?
Compression
Can compression help?
Common Graphics Formats
18GIF – Graphics Interchange Format
Uses compression
Two versions 87a and 89a (animated gif, interlacing)
JPEG – Joint Photographic Experts Group
Different levels of compression
Better for photographs, Less efficient
Open standard
Postscript
Vector, resolution independent
Resolution
19How many pixels per square inch
Higher resolution = more detail
Higher resolution = larger files
Output resolution
Screen = 70 - 90 dpi
Laser Printers = 300 to 600 dpi
Typesetters = 1200-2400 dpi
Higher resolution can be scaled down, lower can’t be scaled up.
Colour Depth
201 bit = black and white (2^1 = 2 colours)
8 bit = 256 colours (2^8 = 256 colours)
Useful colour for games and information
24 bit = 16 million colours
Realistic photo quality images for publication
(2^24 = 16,777,216 colours)